
News
Truck Checks: Apparatus 101: Test your skills
CURRENT ISSUE
Apparatus 101: Test your skills
Truck Checks columnist Don Henry has a holiday treat for readers. In the December issue he offers up a challenging and comprehensive quiz to test your apparatus expertise.
December 5, 2008
By Don Henry
What are emergency vehicle technicians? They are people of many skills – small engine mechanic, automotive and heavy duty technician, plumber with a dash of auto body artist throw in. They are people who are willing to accept the tremendous responsibility for the results of their work. Simply put, unless you walk to the fire, you need these people.
 |
| Pumptack: Pump section, questions 21 to 30. |
 |
| Question 29: Identify the pump. Advertisement
|
 |
| Question 30: Identify the pump. |
 |
| Alternator: Electrical section starts with question 41 |
 |
| Truck checks: Apparatus at the fire.etc training school at Lakeland College enjoy regular maintenance. |
It is very important that we encourage and support the training and recognition of this group of skilled people. The Emergency Vehicle Technician Certification Commission is a group that works to accomplish this outcome. It has numerous exams that can be taken to prove your level of knowledge. Exams on fire apparatus, ARFF law enforcement and ambulance are available. Theses exams are fair but tough. The cost is reasonable. There are two test dates each year, one in October and the other in June. For more information go to www.evtcc.org.
Technicians are sometimes a bit hesitant to attempt these exams. I produced an assessment exam on fire apparatus for those people who would like to get a feel for what these exams are about. I made up 20 questions in each area and then divided the question further into two groups, 10 general knowledge questions about the nuts and bolts and 10 that deal with the NFPA standards used to make and maintain the fire truck. You will need to get your nose into to both the NFPA 1901 and the 1911 if you want to pass these exams.
Give these questions a try. The answers will be posted at www.granitefleet.com/answers.
While you are at the Granite site, look at the fleet maintenance software. If you do well on my questions then sign up for the Emergency Vehicle Technician Certification Commission exams, study hard and good luck.
Meantime, I would like to recognize and congratulate the following people for recently achieving their Master Level EVT status: Dayle Coghlin, Kitchener Fire Department, Ont.; Doug Cox, Vancouver Fire and Rescue Services; Lynn Deacon, London Fire Services, Ont; Barry Dollmaier, Town of Caledon Fire & Emergency Services, Ont; Tom Hooker, Richmond Fire-Rescue, B.C.; Glenn Jones, City of Victoria Fire Department; David Kennedy, Halifax Regional Fire & Emergency Service; Dennis McCarthy, Toronto Fire Services; Gale Myers, Rocky Mountain Phoenix; Terry Santink, Strathmore Fire Department, Alta.; Roger Zanettin, Windsor Fire & Rescue Services; D.W. Scott Urquhart, District of North Vancouver Fire & Rescue Service; Daniel Vieno, St. Catharines Fire and Emergency Services Department, Ont.
■ These first 20 questions deal with design and performance objectives.
1. Fill in the blanks: Apparatus that can flow water under
pressure while moving is referred to as _________________________ and _________________________.
2. Define the term “draft” as it applies to fire apparatus.
3. Define the term “residual” water pressure as it applies to fire apparatus and fire hydrants.
4. Define the term “static” water pressure as it applies to fire apparatus.
5. GVWR stands for:
6. GAWR stands for:
7. GCWR stands for:
8. A soft suction hose can be used to supply a fire pumper directly from a lake or pond.
a. True
b. False
9. A gauge located on the pump panel that can read both a vacuum and a pressure is called:
a. Twin gauge
b. Double gauge
c. Vacuum gauge
d. Compound gauge
10. The term “maximum governed speed” refers to the:
a. Maximum engine r.p.m.
b. Engine high idle
c. Maximum fire pump
shaft speed
d. Fastest forward speed
e. Both a and b
■ Questions 11 to 20 refer to NFPA 1901, 2009 Edition
11. Service brakes must be able to stop a fully loaded apparatus at a speed of 32 kph (20 mph) in a distance not to exceed:
a. 10.7 metres (35 feet)
b. 15 metres (49.2 feet)
c. 20 metres (65.2 feet)
d. Four times the length of the truck
12. To be considered an initial attack pumper, a pumper must have a pump size of at least:
a. 750 litres (198 gallons)
b. 1,000 litres ( 250 gallons)
c. 1,250 litres (330 gallons)
d. 2,000 litres (528 gallons)
13. The apparatus shall be able to maintain a speed of at least 32 kph (20 mph) on a grade of up to _________ per cent.
14. Who determines the maximum engine operating temperature?
a. Fire department
b. Engine manufacturer
c. Apparatus manufacturer
15. The pump to tank fill line on pumps of more than 3785 litres (1,000 gallons) shall be of at least:
a. 300 mm (12 inches)
b. 200 mm (8 inches)
c. 100 mm (4 inches)
d. 50 mm (2 inches)
16. Non-driving steering axles must be capable of a minimum angle of how many degrees?
a. 15
b. 20
c. 25
d. 30
17. Pump water intake valves (excluding tank to pump) must be gated with slow moving valves if they are of what size or larger?
a. 76 mm (3 inches)
b. 65 mm (2.5 inches)
c. 100 mm (4 inches)
d. any intake valve
18. The engine’s fuel tank must hold enough fuel for:
a. 2.5 hours of pumping @ 1035 kPa (150 p.s.i.)
b. 3 hours of pumping @ 1400 kPa (200 p.s.i.)
c. 1 hour of pumping @ 1035 kPa (150 p.s.i.)
d. 3 hours of pumping @ 1035 kPa (150 p.s.i.)
19. By design the braking system must hold a fully loaded vehicle on a grade per cent of at least:
a. 7 per cent
b. 10 per cent
c. 20 per cent
d. 25 per cent
20. All fully loaded apparatus shall be able to attain a minimum top speed on a level road of at least:
a. 80 kph (50 mph)
b. 105 kph (65 mph)
c. 88 kph (55 mph)
d. 72 kph (45 mph)
■ These questions relate to the objectIVEs of the fire pumps
21. When operating the fire pump in the “series/pressure” operation of a two-stage pump, the pump will deliver:
a. Double the pressure, half the volume of water
b. Half the pressure, double the volume of water
c. Double the pressure, double the volume of water
d. Half the volume, half the pressure of water
22. When operating the fire pump in the “volume/parallel” operation of a two-stage pump, the pump will deliver:
a. Double the pressure, half the volume of water
b. Half the pressure, double the volume of water
c. Double the pressure, double the volume of water
d. Half the volume, half the pressure of water
23. A pumper has to be subjected to a strong water hammer. The master pump gauge will not return to zero but reads 100 kPa. (14.5 psi) You should:
a. Recalibrate the gauge
b. Replace the gauge
c. Advise the operators to just subtract 100 kPa (14.5 psi) from all readings
d. Water hammers the fire pump with a reverse flow of water to re-centre the gauge
24. Technician A wants to adjust a fire pump packing when operating under pressure and flow until no water drips from the packing. Technician B says that pump packing can be adjusted with only static water pressure from the truck’s water tanks. Who is correct?
a. Technician A
b. Technician B
c. Both technicians
d. Neither technician
25. The most common reason for failing a fire pump service test during the high pressure, low flow is:
a. Engine low on power
b. Excessive wear (clearance) between the impeller hub and wear ring
c. Transmission slipping in low gear
d. Transmission oil
overheating
e. Pump losing prime
26. A pitot gauge is used to measure what?
a. Engine oil pressure
b. Water pump flow during
a flow test
c. Air-flow rates
d. Small pilots
27. The dry vacuum test is performed the first time with:
a. Intake suction hose in the water source (pond, lake) and open
b. Discharge valves open but capped
c. Discharge valves closed but capped on tight as possible
d. Intake ports capped, but intake valves open
e. Intake suction hose connected but not capped
28. A mechanical r.p.m. counter on the fire pump transfer case reads excessively different than the engine r.p.m. on the pump panel during pumping. This is:
a. This is normal, you often have to multiply by a factor of ten times.
b. Caused because the slippage in the transmission
c. Caused because one of the gauges is defective
d. Because the transmission is in overdrive when pumping
e. Both b and c
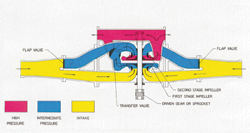
29. The picture above shows the pump in:
a. Parallel/volume
b. Series/pressure
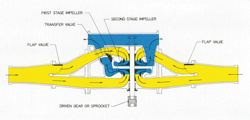
30. The picture above shows the pump in:
a. Parallel/volume
b. Series/pressure
■ The following questions refer to NFPA 1901, 2009 Edition:
31. At less than 2,000 feet above sea level, a priming device must be able to reach a maximum of how many inches of mercury during the vacuum test
a. 18 inches
b. 20 inches
c. 22 inches
d. 25 inches
32. The priming vacuum must be held for a minimum of how many minutes?
a. Two minutes
b. Three minutes
c. Five minutes
d. No time is referred to in the standard
33. During the vacuum test, it is permissible to lose some vacuum. What is the maximum allowable amount?
a. Five inches
b. 10 inches
c. 14.7 inches
d. All of the vacuum
34. Priming devices on new fire pumps must now to able to operate with what type of lubrication?
a. No lubrication
b. Biodegradable nontoxic lubricant
c. 10-weight motor oil
d. Synthetic motor oil
e. A or B
35. For pumps of 4732 L/min. (1250 gpm) or less, the time to prime from draft shall not exceed:
a. 15 seconds
b. 30 seconds
c. 45 seconds
d. 60 seconds
36. For pumps larger than 6000 L/min. (1500 gpm), the time to prime is extended by:
a. 10 seconds
b. 15 seconds
c. 30 seconds
d. 45 seconds
37. All pumps must have a working pressure control system. This system must not allow the pressure to rise by more than what amount when a discharge valve is closed no more rapidly than in 3 seconds and not more slowly than in 10 seconds?
a. 30 p.s.i.
b. 10 p.s.i.
c. 45 p.s.i.
d. 12 p.s.i.
38. During the above test, the pump pressure must
a. 70 psi to 300 psi net pump pressure
b. 90 psi to 320 psi net pump pressure
c. 100 psi to 350 psi
d. Makes no difference
39. The overload pump test shall be conducted for:
a. 1,138 kPa (165 p.s.i.) for 10 minutes
b. 1,035 kPa (150 p.s.i.) for 15 minutes
c. 1,380 kPa (200 p.s.i.) for 10 minutes
d. there is no such test, overload test is for springs
40. During the annual service test, is it permissible to remove engine covers, raise hoods, or remove panels from the truck?
a. Yes
b. No
c. Only if you need to keep the engine from overheating
■ The following questions deal with the electrical objectives
41. The normal open cell voltage (OCV) for a six cell battery after the surface charge has been removed is:
a. 12.0 to 13.8 volts
b. 12.4 to 12.8 volts
c. 13.0 to 14.4 volts
d. never lower than 9.6 volts
42. Define cold cranking amps (CCA) in regard to batteries.
43. Define reserve capacity (RC) in regard to batteries.
44. Why is RC more important to a fire truck than CCA?
a. Because fire trucks start in warm fire halls
b. Because if the alternator fails at a fire, you want to know how long you can operate with only the batteries
c. Because fire trucks are easy to boost
d. Both A and B
e. Both A and C
45. Define voltage drop.
46. What is the purpose of a load-shed device?
a. To shut off excessive loads as battery voltage increases
b. To shut off excessive loads as battery voltage decreases
c. To turn on loads as battery voltage decreases
47. An alternator has a lower than normal amperage output. The technician suspects a defective diode. If one defective diode was open, the alternator output would be:
a. 10 per cent less
b. 30 per cent less
c. 60 per cent less
d. No effect
Print this page
Advertisement
- FlashPoint: Admitting our mistakes and learning from them
- Trainer’s Corner: Containing the fire spread